Using diagnostic
classification models
to Improve Instructional Decision-Making
Who am I?
W. Jake Thompson, Ph.D.
- Assistant Director of Psychometrics
- ATLAS | University of Kansas
- Research: Applications of diagnostic psychometric models
- Lead psychometrician and Co-PI for the Dynamic Learnings Maps assessments
- PI for an IES-funded project to develop software for diagnostic models
Acknowledgements
The research reported here was supported by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through Grants R305D210045 and R305D240032 to the University of Kansas Center for Research, Inc., ATLAS. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent the views of the the Institute or the U.S. Department of Education.

What are diagnostic models?

- Traditional assessments and psychometric models measure an overall skill or ability
- Assume a continuous latent trait
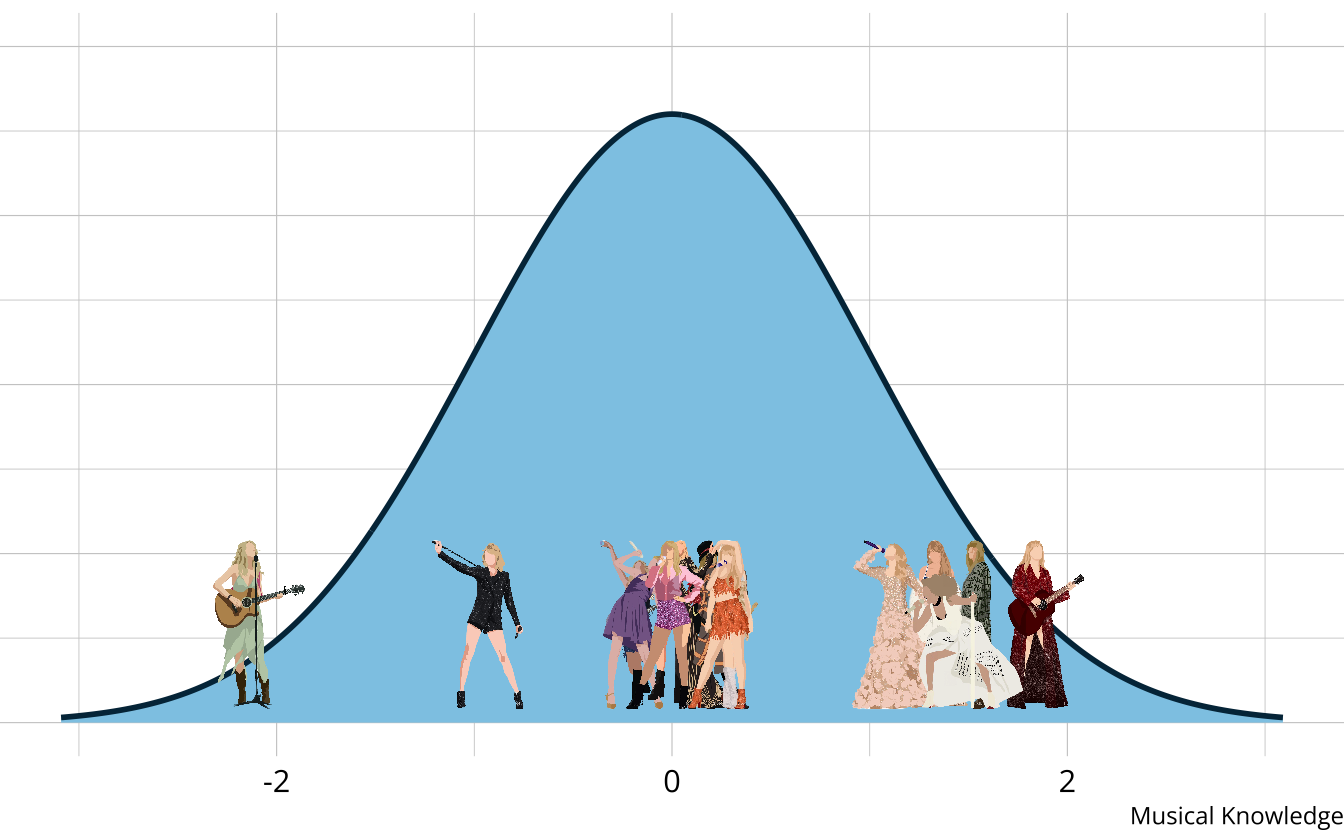
- The output is a weak ordering due to error in estimates
- Confident Taylor Swift (debut) is the worst
- Not confident on ordering toward the middle of the distribution

- Limited in the types of questions that can be answered.
- Why is Taylor Swift (debut) so low?
- What aspects do each era demonstrate proficiency or competency of?
- How much skill is “enough” to be competent?

Diagnostic measurement
- Designed to be multidimensional
- No continuum of student achievement
- Categorical constructs
- Usually binary (e.g., master/nonmaster, proficient/not proficient)
- Several different names in the literature
- Diagnostic classification models (DCMs)
- Cognitive diagnostic models (CDMs)
- Skills assessment models
- Latent response models
- Restricted latent class models
Diagnostic music assessment
- Rather than measuring overall musical knowledge, we can break music down into set of skills or attributes
- Songwriting
- Production
- Vocals
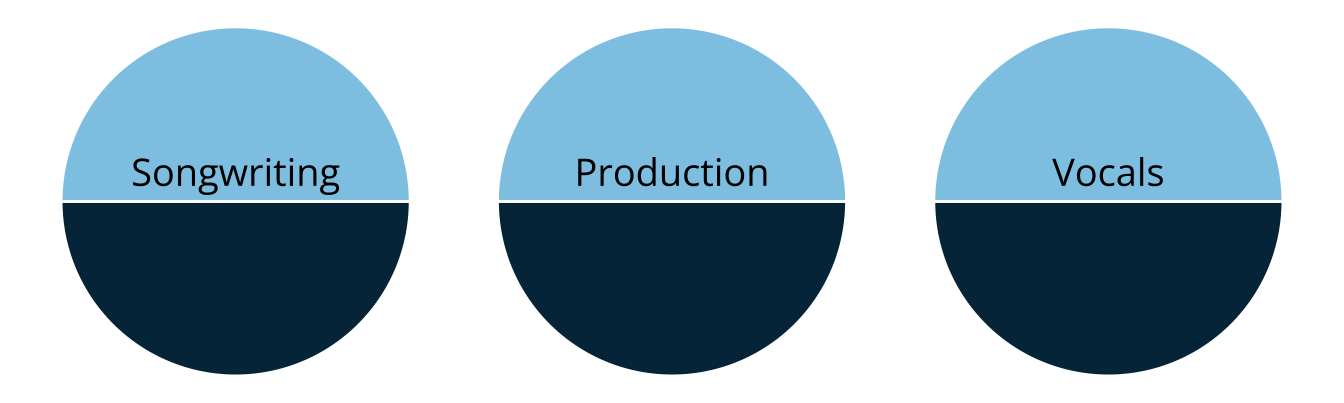
- Attributes are categorical, often dichotomous (e.g., proficient vs. non-proficient)
Diagnostic classification models
- DCMs place individuals into groups according to proficiency of multiple attributes
| songwriting | production | vocals | |
|---|---|---|---|
Benefits of DCMs
- Fine-grained, multidimensional results. Answer more questions:
- Why is Taylor Swift (debut) so low?
- Subpar songwriting, production, and vocals
- What aspects are albums competent/proficient in?
- DCMs provide classifications directly
- Why is Taylor Swift (debut) so low?
- High reliability with fewer items
- Less information need to classify than to place precisely along a scale
| songwriting | production | vocals | |
|---|---|---|---|
Using DCMs to improve student
outcomes
Applications in educational assessment
-
Dynamic Learning Maps®
- Achievement assessment for students with the most significant cognitive disabilities
- Currently used by 24 states for accountability reporting to the U.S. Department of Education
-
Pathways to Instructionally Embedded assessment
- Competitive Grant for State Assessment award from the U.S. Department of Education
- Partnership between ATLAS and the Missouri Department of Elementary and Secondary Education

Thompson & Clark (2024): Improving instructional decision-making using diagnostic classification models
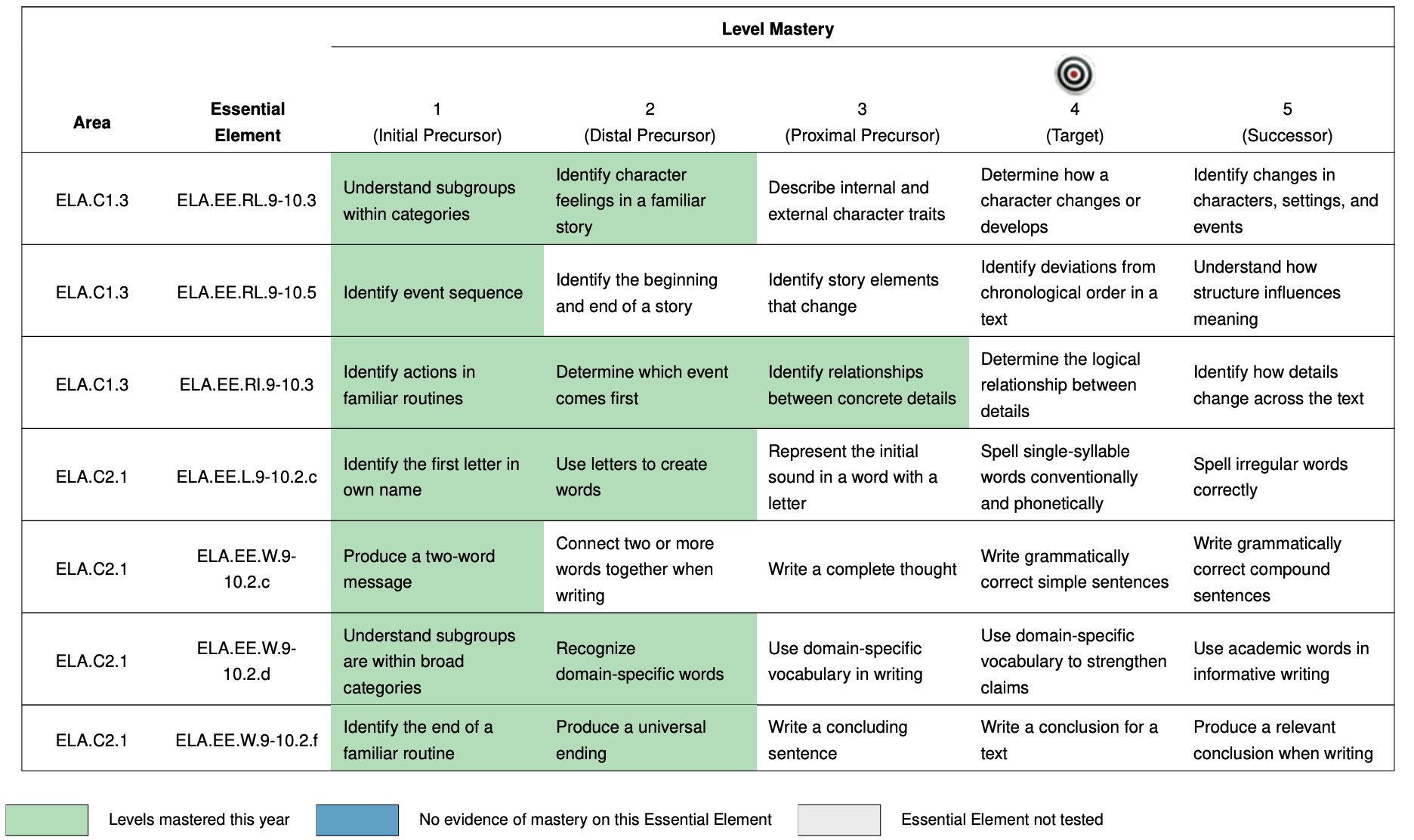
Dynamic Learning Maps (DLM)
-
Assessment items are aligned to alternate academic achievement standards
- Academic content available at multiple levels of complexity for each standard
- Results reported as profile of skills mastered within each standard
Teachers have flexibility to assign the level most appropriate for their student
Skills within each standard follow a linear hierarchy
Results are used throughout the year to inform individual education program (IEP) plans and instructional planning (Clark et al., 2023)
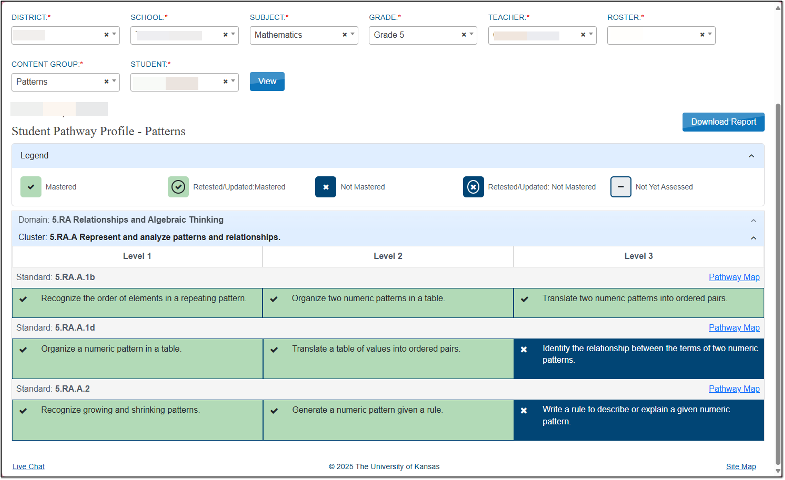
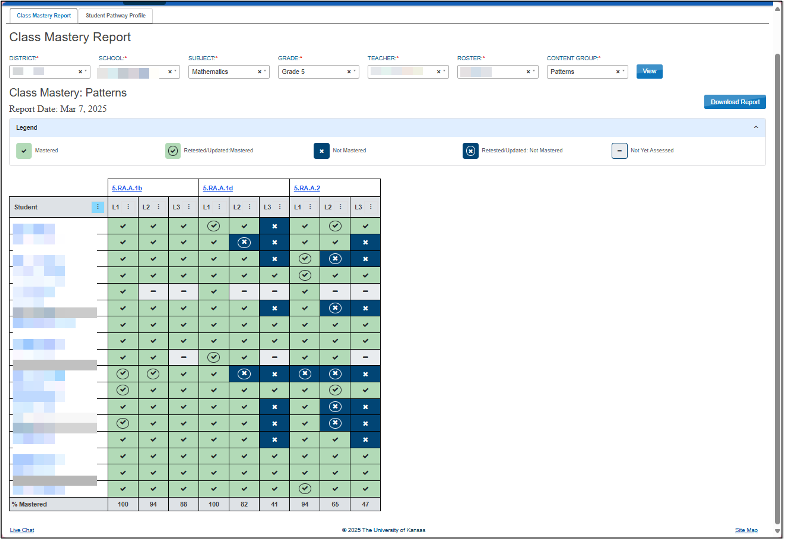
DLM reporting
Pathways to Instructionally Embedded assessment (PIE)
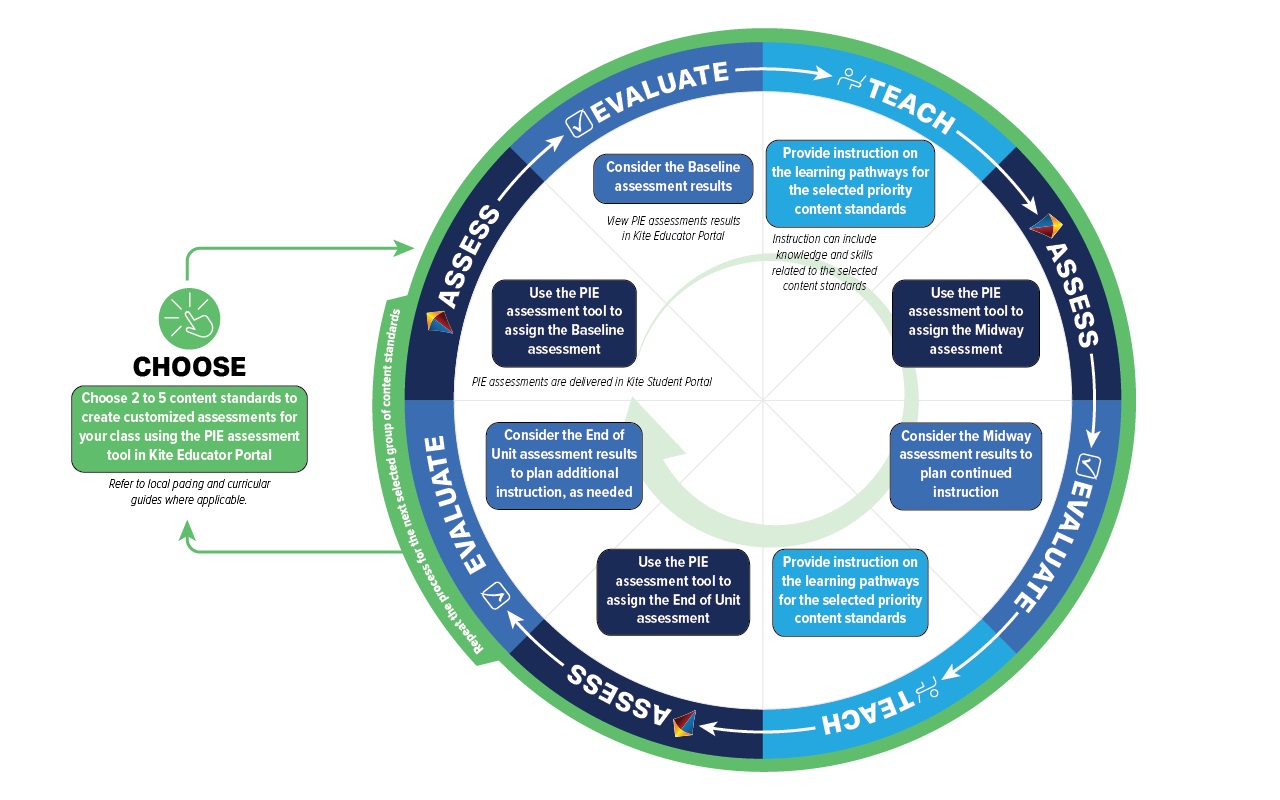
Pathway levels were developed for grade 5 mathematics to identify precursor concepts and skills related to the learning target of each standard
-
Students are assessed on each pathway level within the standard over the course of an instructional cycle
- Baseline: Level 1
- Midway: Level 1 (retest) + Level 2
- End-of-unit: Level 2 (retest) + Level 3
Teachers can use results to implement small group or individualized instructional strategies (ATLAS, 2025)
PIE instructional cycle
PIE reporting
PIE reporting
Additional research applications
Evaluate educator understanding of concepts to inform professional development opportunities (e.g., Bradshaw et al., 2014, Izsák et al., 2019)
Understand profiles of mental health symptoms (e.g., Tan et al., 2023)
Evaluate the effect of interventions as transitions in proficiency status (e.g., Madison & Bradshaw, 2018)
How to get started…

Improved software for diagnostic models
measr: R package for Bayesian psychometric measurement using Stan
-
Easily specify and estimate a DCM
- Wide variety of DCMs (e.g., LCDM, DINA, C-RUM)
- Defined attribute relationships and dependencies
- Supports maximum likelihood and full MCMC model estimation
-
Powerful model evaluation tools
- Model fit using posterior predictive model checks
- Model comparisons with leave-one-out cross validation
- Classification accuracy and consistency metrics
More information: https://measr.r-dcm.org